reading-notes
What are Objects in JavaScript?
Objects, in JavaScript, is it’s most important data-type and forms the building blocks for modern JavaScript. These objects are quite different from JavaScript’s primitive data-types(Number, String, Boolean, null, undefined and symbol) in the sense that while these primitive data-types all store a single value each (depending on their types).
- Objects are more complex and each object may contain any combination of these primitive data-types as well as reference data-types.
An object, is a reference data type. Variables that are assigned a reference value are given a reference or a pointer to that value. That reference or pointer points to the location in memory where the object is stored. The variables don’t actually store the value.
Loosely speaking, objects in JavaScript may be defined as an unordered collection of related data, of primitive or reference types, in the form of “key: value” pairs. These keys can be variables or functions and are called properties and methods, respectively, in the context of an object.
An object can be created with figure brackets {…} with an optional list of properties. A property is a “key: value” pair, where a key is a string (also called a “property name”), and value can be anything.
Inherited Properties
Inherited properties of an object are those properties which have been inherited from the object’s prototype, as opposed to being defined for the object itself, which is known as the object’s Own property. To verify if a property is an objects Own property, we can use the hasOwnProperty method.
Property Attributes
Data properties in JavaScript have four attributes.
-
value: The property’s value.
-
writable: When true, the property’s value can be changed
-
enumerable: When true, the property can be iterated over by “for-in” enumeration. O
Otherwise, the property is said to be non-enumerable.
- configurable: If false, attempts to delete the property, change the property to be an access-or property, or change its attributes (other than [[Value]], or changing [[Writable]] to false) will fail.
Creating Objects
There are several ways or syntax’s to create objects. One of which, known as the Object literal syntax, we have already used. Besides the object literal syntax, objects in JavaScript may also be created using the constructors, Object Constructor or the prototype pattern.
Object literal
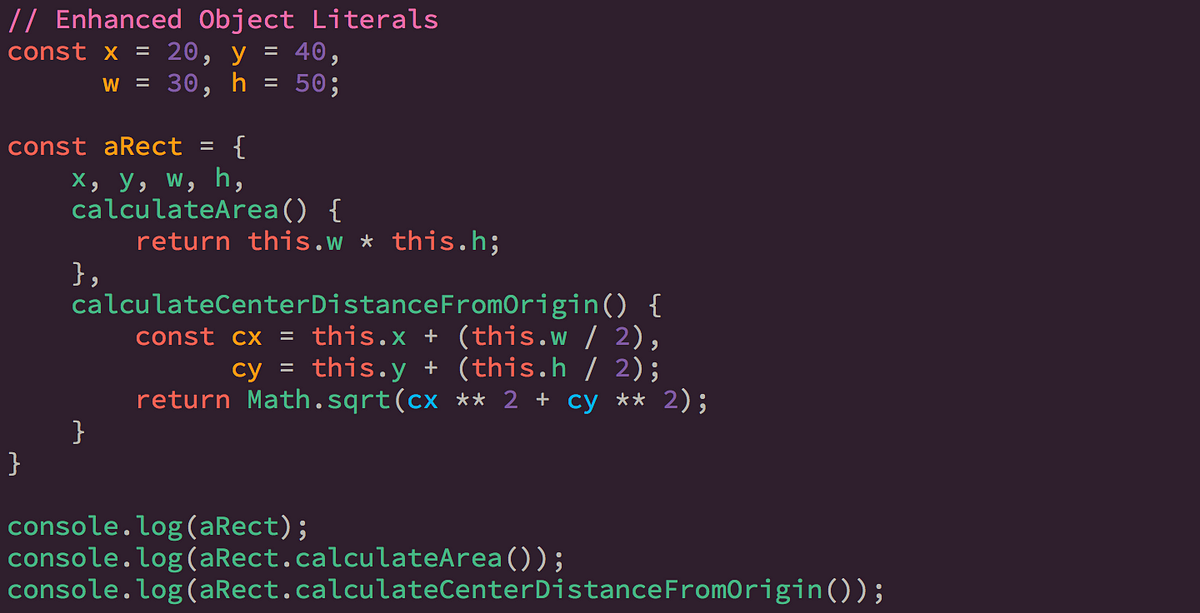
Object literal enhancement is used to group variables from the global scope and form them into javascript objects. It is the process of restructuring or putting back together.
Using the Object literal syntax : Object literal syntax uses the {…} notation to initialize an object an its methods/properties directly.
Document Object Model
The HTML DOM (Document Object Model)
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
The HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects:

With the object model, JavaScript gets all the power it needs to create dynamic HTML:
-
JavaScript can change all the HTML elements in the page
-
JavaScript can change all the HTML attributes in the page
-
JavaScript can change all the CSS styles in the page
-
JavaScript can remove existing HTML elements and attributes
-
JavaScript can add new HTML elements and attributes
-
JavaScript can react to all existing HTML events in the page
-
JavaScript can create new HTML events in the page
What is the DOM?
The DOM is a W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard.
The DOM defines a standard for accessing documents:
“The W3C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language-neutral interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document.”
The W3C DOM standard is separated into 3 different parts:
-
Core DOM - standard model for all document types
-
XML DOM - standard model for XML documents
-
HTML DOM - standard model for HTML documents
What is the HTML DOM?
The HTML DOM is a standard object model and programming interface for HTML. It defines:
-
The HTML elements as objects
-
The properties of all HTML elements
-
The methods to access all HTML elements
-
The events for all HTML elements
In other words: The HTML DOM is a standard for how to get, change, add, or delete HTML elements.