reading-notes
Lists in HTML
HTML lists allow web developers to group a set of related items in lists.
Three kinds of lists
Ordered lists
An ordered list starts with the ol tag. Each list item starts with the li tag.


Unordered lists
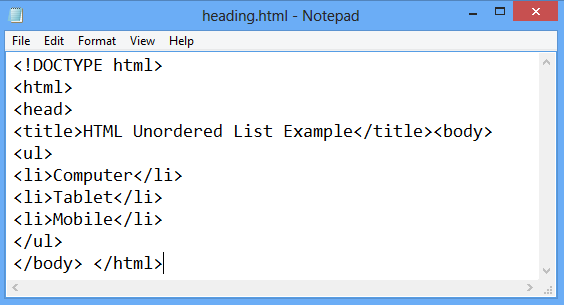
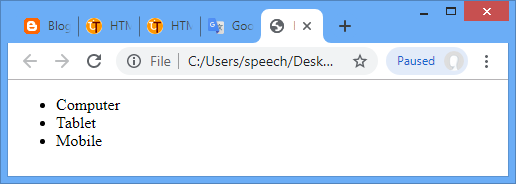
An unordered list starts with the ul tag. Each list item starts with the li tag.
Nested lists
A nested list or a sublist is a list within a list. The trick to marking nested lists up correctly in HTML is to recognize that the sublist is actually a child of a list item and not of a list.


CSS box model
In CSS, the term “box model” is used when talking about design and layout.
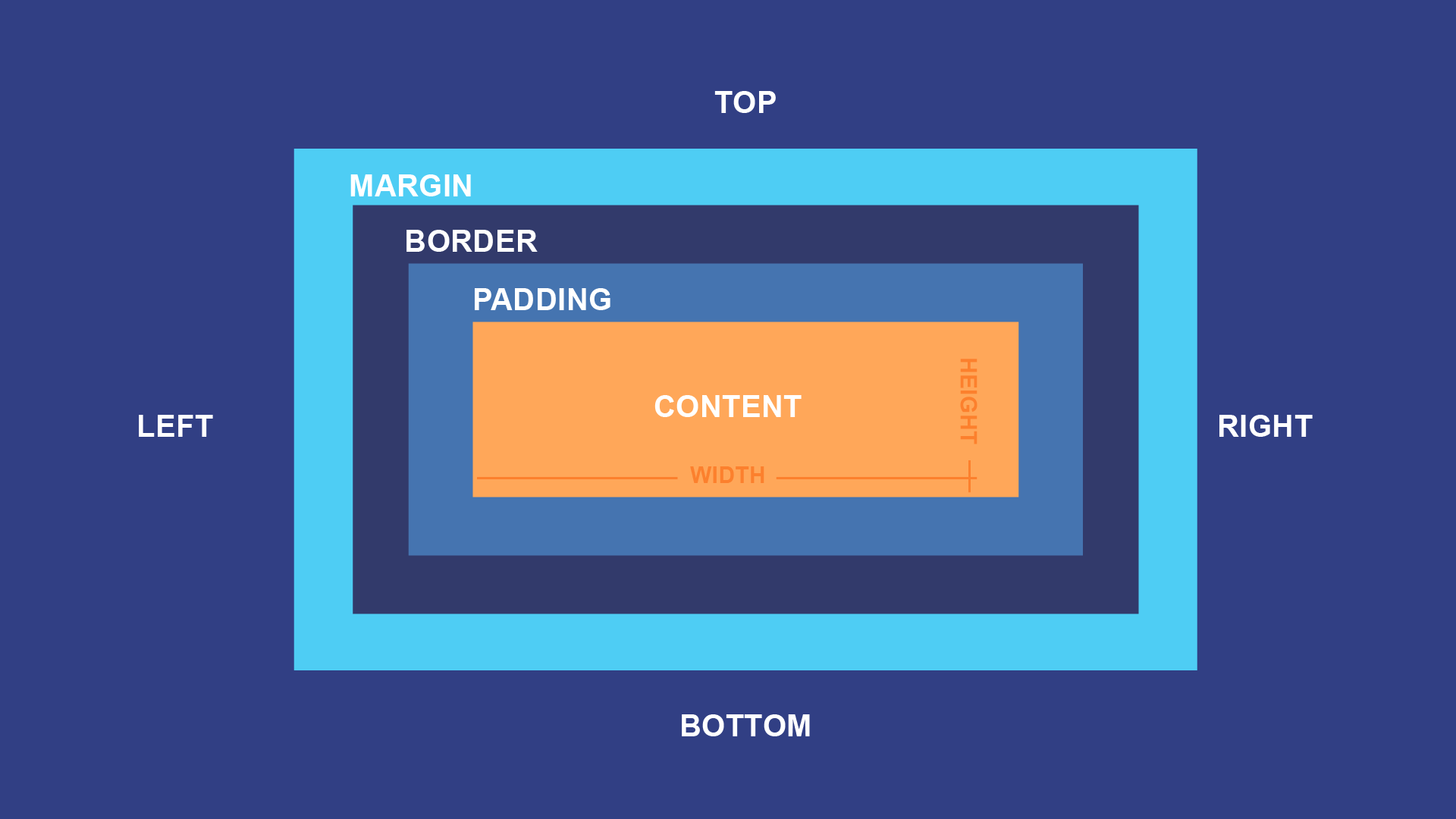
The CSS box model is essentially a box that wraps around every HTML element. It consists of: margins, borders, padding, and the actual content.
-
Content - The content of the box, where text and images appear.
-
Padding - Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent.
-
Border - A border that goes around the padding and content.
-
Margin - Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent.
The box model allows us to add a border around elements, and to define space between elements.

JavaScript
JavaScript (“JS” for short) is a full-fledged dynamic programming language that can add interactivity to a website. It was invented by Brendan Eich (co-founder of the Mozilla project, the Mozilla Foundation, and the Mozilla Corporation).
JavaScript is versatile and beginner-friendly. With more experience, you’ll be able to create games, animated 2D and 3D graphics, comprehensive database-driven apps, and much more!
JavaScript itself is relatively compact, yet very flexible. Developers have written a variety of tools on top of the core JavaScript language, unlocking a vast amount of functionality with minimum effort. These include:
Browser Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) built into web browsers, providing functionality such as dynamically creating HTML and setting CSS styles; collecting and manipulating a video stream from a user’s webcam, or generating 3D graphics and audio samples. Third-party APIs that allow developers to incorporate functionality in sites from other content providers, such as Twitter or Facebook. Third-party frameworks and libraries that you can apply to HTML to accelerate the work of building sites and applications. It’s outside the scope of this article—as a light introduction to JavaScript—to present the details of how the core JavaScript language is different from the tools listed above. You can learn more in MDN’s JavaScript learning area, as well as in other parts of MDN.
The section below introduces some aspects of the core language and offers an opportunity to play with a few browser API features too. Have fun!
A Hello world! example JavaScript is one of the most popular modern web technologies! As your JavaScript skills grow, your websites will enter a new dimension of power and creativity.
However, getting comfortable with JavaScript is more challenging than getting comfortable with HTML and CSS. You may have to start small, and progress gradually. To begin, let’s examine how to add JavaScript to your page for creating a Hello world! example.
Decisions and loops
Definition and Usage
The if/else statement executes a block of code if a specified condition is true. If the condition is false, another block of code can be executed.
The if/else statement is a part of JavaScript’s “Conditional” Statements, which are used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
In JavaScript we have the following conditional statements:
Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true
Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false
Use else if to specify a new condition to test, if the first condition is false
Use switch to select one of many blocks of code to be executed
Syntax
The if statement specifies a block of code to be executed if a condition is true
The else statement specifies a block of code to be executed if the condition is false
The else if statement specifies a new condition if the first condition is false
The switch statement executes a block of code depending on different cases.
The switch statement is a part of JavaScript’s “Conditional” Statements, which are used to perform different actions based on different conditions. Use switch to select one of many blocks of code to be executed. This is the perfect solution for long, nested if/else statements.
The switch statement evaluates an expression. The value of the expression is then compared with the values of each case in the structure. If there is a match, the associated block of code is executed.
The switch statement is often used together with a break or a default keyword (or both). These are both optional:
The break keyword breaks out of the switch block. This will stop the execution of more execution of code and/or case testing inside the block. If break is omitted, the next code block in the switch statement is executed.
The default keyword specifies some code to run if there is no case match. There can only be one default keyword in a switch. Although this is optional, it is recommended that you use it, as it takes care of unexpected cases.
The return statement stops the execution of a function and returns a value from that function.